Satellite Imagery
We distribute a wide range of cost-effective and affordable satellite images.

Orthorectification
Most types of raw satellite imagery require geometric correction to remove terrain distortions. We utilize the 30 m Aster GDEM for the most of the orthorectification work.

Mosaicking
Due to seasonal variations and the illumination conditions, different sets of satellite images may look different. We offer professional mosaicking services to produce seamless and color balanced image mosaics.

Pan-sharpening
Powered by FuzeGo™
Pansharpening is a process of merging high-resolution panchromatic and lower resolution multispectral imagery to create a single high-resolution color image.

Atmospheric Correction
Need spectral reflectance data? We provide robusted DN to Reflectance Conversion Service which removes atmospheric effects from your satellite image.
Order your satellite imagery now
For more than 30 years, Geocarto International Centre Ltd. has been a leading distributor of satellite remote sensing data and provider of image processing services in the Asia Pacific region.


Deimos-2
Deimos Imaging S.L.U.
Launched on June 19, 2014, Deimos-2 satellite is high resolution (75 cm pan-sharpened) multispectral optical satellite
| Panchromatic | 75 cm |
| Multispectral 4 | 3 m |

GeoEye-1
Maxar Technology
GeoEye-1 is a very high resolution satellite launched in 2008 and is owned and operated by DigitalGlobe. GeoEye collects images at 41 cm panchromatic and 1.65 m multispectral resolution.
| Panchromatic | 50 cm |
| Multispectral 4 | 2 m |

Archived
QuickBird
Maxar Technology
QuickBird, launched on October 18, 2001, offered 61 cm resolution panchromatic data and 2.44 m resolution multispectral data with high geolocational accuracy.
| Panchromatic | 61 cm |
| Multispectral 4 | 2.44 m |

WorldView-1
Maxar Technology
WorldView-1, launched on September 18 2007, is the first earth observations satellite owned by DigitalGlobe.
| Panchromatic | 50 cm |

WorldView-2
Maxar Technology
WorldView-2, launched on October 8 2009, is the first high-resolution 8-band multispectral commercial satellite.
| Panchromatic | 40/50 cm |
| Multispectral 8 | 1.6/2.0 m |

WorldView-3
Maxar Technology
WorldView-3, launched on August 13, 2014, is the industry's first multi-payload, super-spectral, high-resolution commercial satellite.
| Panchromatic | 30/40/50 cm |
| Multispectral 8 | 1.2/1.6/2.0 m |
| Multispectral 8 | 7 m |

WorldView-4/GeoEye-2
Maxar Technology
WorldView 4, formerly known as GeoEye 2, is a commercial high-rsolution earth observation satellite operated by DigitalGlobe. It provides 31 cm panchromatic resolution, and 1.24 m multispectral resolution.
| Panchromatic | 31 cm |
| Multispectral 4 | 1.24 m |

DubaiSat-2
MBRSC
DubaiSat-2 is the second Earth observation satellite of United Arab Emirates Institution for Advanced Science and Technology (EIAST).
| Panchromatic | 1 m |
| Multispectral 4 | 4 m |

Jilin 01
Chang Guang Technology
Jilin-1 is a constellation of earth observation satellites from China , which will deliver panchromatic data of better than 1m resolution, and multispectral data of better than 4m resolution for commercial applications.
| Panchromatic | 72 / 75 cm |
| Multispectral 5 | 2.88 / 3 m |

KOMPSAT-3
KARI
KOMPSAT-3 is an optical sub-meter resolution Korean observation mission of KARI (Korea Aerospace Research Institute). It was launched on May 17, 2012.
| Panchromatic | 70 cm |
| Multispectral 4 | 2.8 m |

KOMPSAT-3A
KARI
Launched on March 25, 2015, Kompsat-3A (Korean Multipurpose Satellite), is an optical satellite with less than half meter product resolution by KARI (Korea Aerospace Research Institute).
| Panchromatic | 55 cm |
| Multispectral 4 | 2.2 m |

KazEOSat-01
Kazakhstan Gharysh Sapary
KazEOSat-01 is a high resolution Earth observation satellite of 1m panchromatic resolution and 4m multispectral resolution.
| Panchromatic | 1 m |
| Multispectral 4 | 4 m |

KazEOSat-02
Kazakhstan Gharysh Sapary
KazEOSat-02 is a medium resolution Earth observation satellite of 6.5m multispectral resolution.
| Multispectral 5 | 6.5 m |

Pléiades-1A
AIRBUS Defence & Space
Pleiades 1A and Pleiades 1B, launched on December 17, 2011 and December 2, 2012 respectively, operate as a constellation in the same orbit, phased 180 degrees apart.
| Panchromatic | 50 cm |
| Multispectral 4 | 2 m |

Pléiades-1B
AIRBUS Defence & Space
Pleiades 1A and Pleiades 1B, launched on December 17, 2011 and December 2, 2012 respectively, operate as a constellation in the same orbit, phased 180 degrees apart.
| Panchromatic | 50 cm |
| Multispectral 4 | 2 m |

SPOT-6/7
AIRBUS Defence & Space
SPOT-7 and SPOT-6 launched on September 9, 2012 are operated by AirBus Defence and Space, France.
| Panchromatic | 1.5 m |
| Multispectral 4 | 6 m |

SuperView-1
Space Will Technology
SuperView-1, launched on December 28 2016, is a high resolution commercial satellites constellation owned by Space View.
| Panchromatic | 50 cm |
| Multispectral 4 | 2 m |
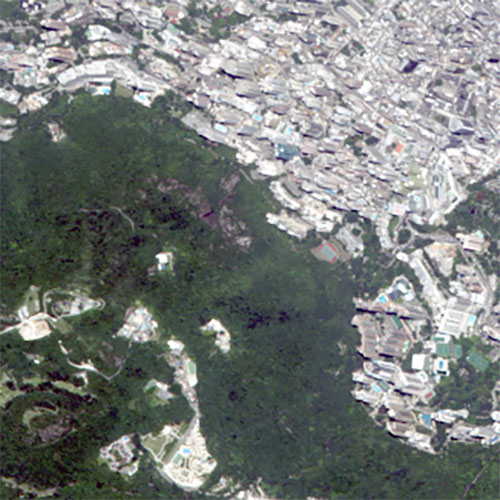
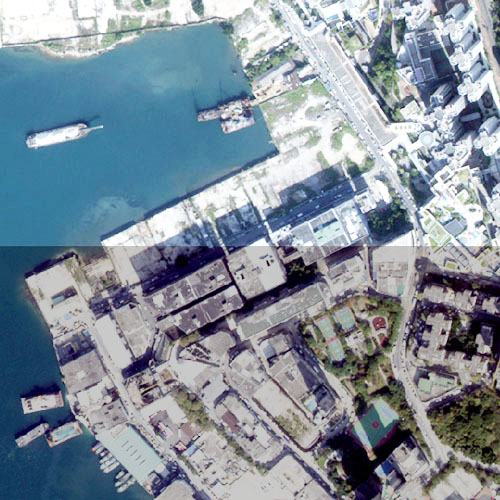
Satellite Imagery Samples
Want to know what can be revealed in a high resolution satellite imagery?
The following are a range of imagery product samples available. Please contact us if you would like to get some image samples related to your activity.
Estimating the Suitable Order Area
Want to know how many satellite data you should order? You can easily get an estimate of your AOI's area under a minute.

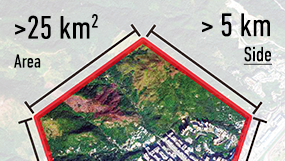
AOI Area Estimator
Easily get an estimate of your AOI's area under a minute.
Please select an AOI from the list to view polygon details.
Corona
America's First Satellite Program
Corona, USA's first operational intelligence satellite, carried sophisticated optical cameras (KH-4B system) to acquire imagery of the Earth from space at an altitude of 80 nautical miles (150 km). It was launched in 1967. The mission life of the system was 19 days. The best quality resolution of 6 feets (2-metre) can be enlarged nearly 40 times up to 1:7,500 from the original film at a nominal scale of 1:247,500.
Declassified in 1994, the photos taken by the satellite constitute a valuable source of historical information for study of environmental changes.

Image copyright NRO
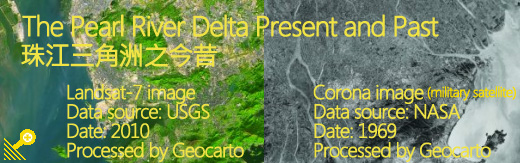
The Pearl River Delta
Corona mosaic
13 December, 1969
Data available from the U.S. Geological Survey.
Processed and Distributed by Geocarto.
The Pearl River Delta
Landsat-8 mosaic
2011
Landsat imagery courtesy of NASA.
Processed and Distributed by Geocarto.
Landsat program
The world's longest continuously acquired collection of land remote sensing data.
Landsat was called ERTS (Earth Resources Technology Satellites) when it was first launched in 1972. This series of satellites was renamed Landsat in 1995. Administered by USGS/NASA, Lansat-5 acquired only colour images of 30-metre resolution. Landsat-7, which launched on April 15, 1999, is orbiting the Earth at an altitude of 705 km. It acquires black and white images with a resolution of 15-metre and colour images with a resolution of 30-metre.
Unlike the Corona satellite which captured imagery on photographic films, Landsat satellites carry sensors to collect electromagnetic radiation reflected from the ground. The data ware is converted into electrical signals and then transmitted in digital form to a ground receiving station. These digital data are subsequently processed to generate images.
The imagery is composed of a matrix of pixels. Each pixel represents the amount of light within a spectral band reflected from the Earth’s surface. Using various combinations of spectral bands, different techniques of image processing and enhancement as well as merging of different remotely sensed data, spectacular images can be generated to highlight particular features to facilitate interpretation and analysis.

Landsat imagery courtesy of NASA.